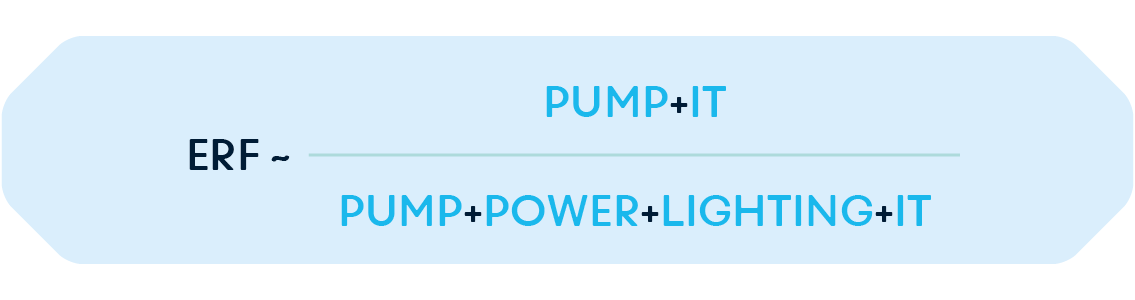PUE Energy Efficiency Savings Calculator
Determine how much you can save by improving data centre efficiency.
Enter Current PUE
PUE
Enter Desired PUE
PUE
kW/h Cost
€
Total IT Load
kW
Current Efficiency Level
Total IT Load
—
Total Facility Load
—
Desired Efficiency Level
Desired IT Load
—
Desired Facility Load
—
Less kW/h Use
1 Year Savings
—
5 Year Savings
—
10 Year Savings
—
Less Power Cost
1 Year Savings
—
5 Year Savings
—
10 Year Savings
—
Less Carbon Tons
1 Year Savings
—
5 Year Savings
—
10 Year Savings
—
Less Homes
1 Year Savings
—
5 Year Savings
—
10 Year Savings
—
| PUE | DCiE | Level of Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| 3.0 | 40% | Very Inefficient |
| 2.5 | 40% | Inefficient |
| 2.0 | 50% | Average |
| 1.5 | 67% | Efficient |
| 1.2 | 83% | Very Efficient |
ERF – ENERGY RECOVERY FACTOR
Energy Recovery Factor is a metric to quantify the effectiveness of heat recovery and reuse from data centres. Formally it is the ratio of the energy that is reused outside of the data centre to the total energy used by the data centre;

In the context of estimating the maximum achievable ERF for the Nexalus-based solution, the total energy must first be approximated;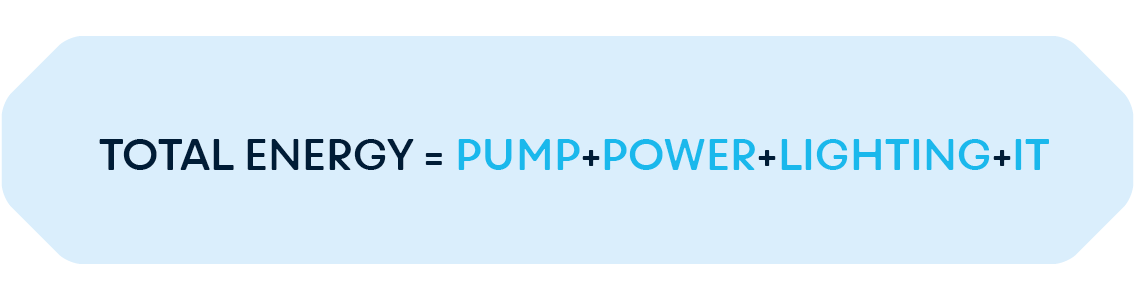
Where Pump is the energy required for pumping the water coolant, Power refers to the switchgear and distribution type equipment, lighting being a general term for peripheral building baseload and IT refers to the energy consumption by the servers for compute purposes.
In an ideal scenario, where all recoverable energy is reused and the pump efficiency is neglected as a first approximation, it will be approximately equate to;
 Resulting in:
Resulting in: